What is Physical Computing?
-
Where the physical world interfaces with computing.
-
Expanding input though sensors.
-> More than touch interfaces and keyboard/mouse.
-
Expanding output through actuators.
-> More than displays.
Inputs & Outputs
Inputs - sensors
- Components that sense properties of the physical world
-
Different ways to convert physical properties into electrical signals
-
Light
-
Simple/ complex touch
-
Temperature
-
Magnetism
-
Sound
-
simple / complex pictures
-
-
Wide variety of sensors
-
simple to complex
-
cheap to expensive
-
Outputs - actuators
- Components that change properties in the physical world
-
Different conversions of electrical signals into physical properties
-
Light
-
Sound
-
Displays
-
Motion
-
Signals
Digital vs Analog
-
Analog signals are continuous with infinitely smooth transitions
-
Digital signals are fixed "steps" with a set resolution
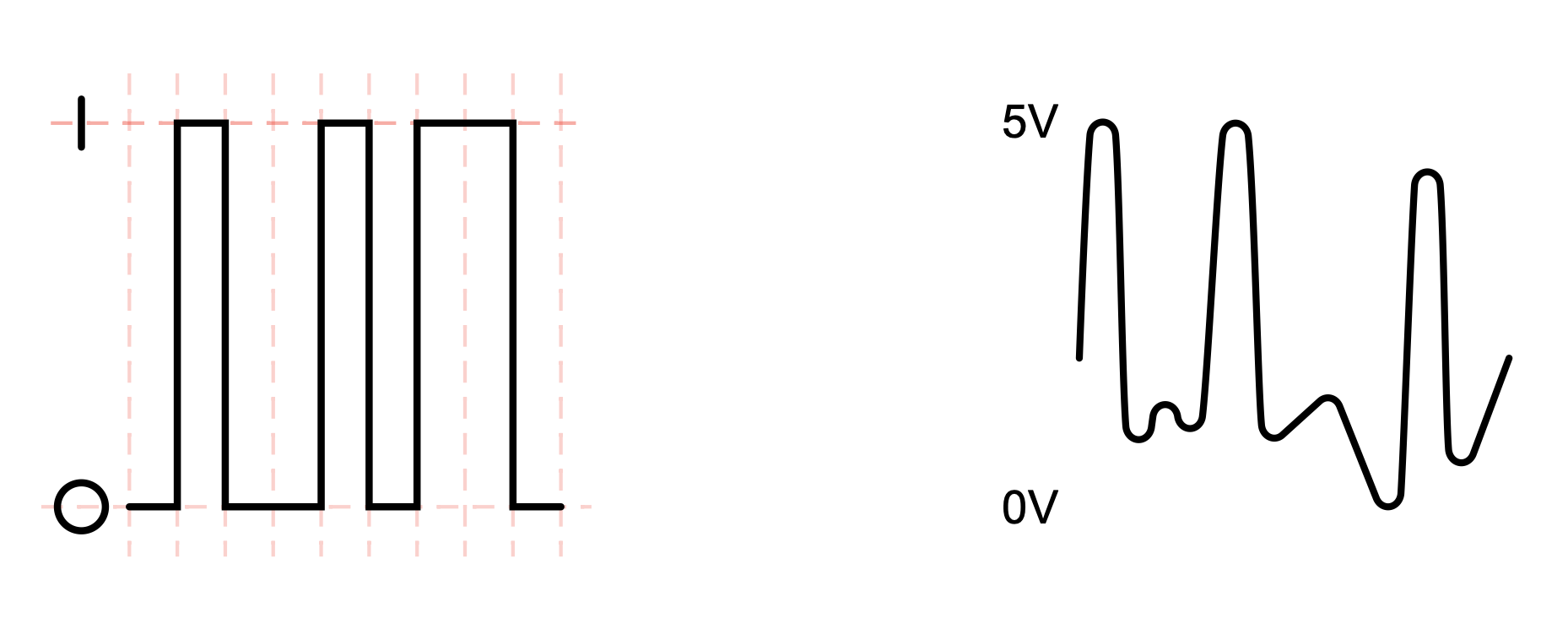
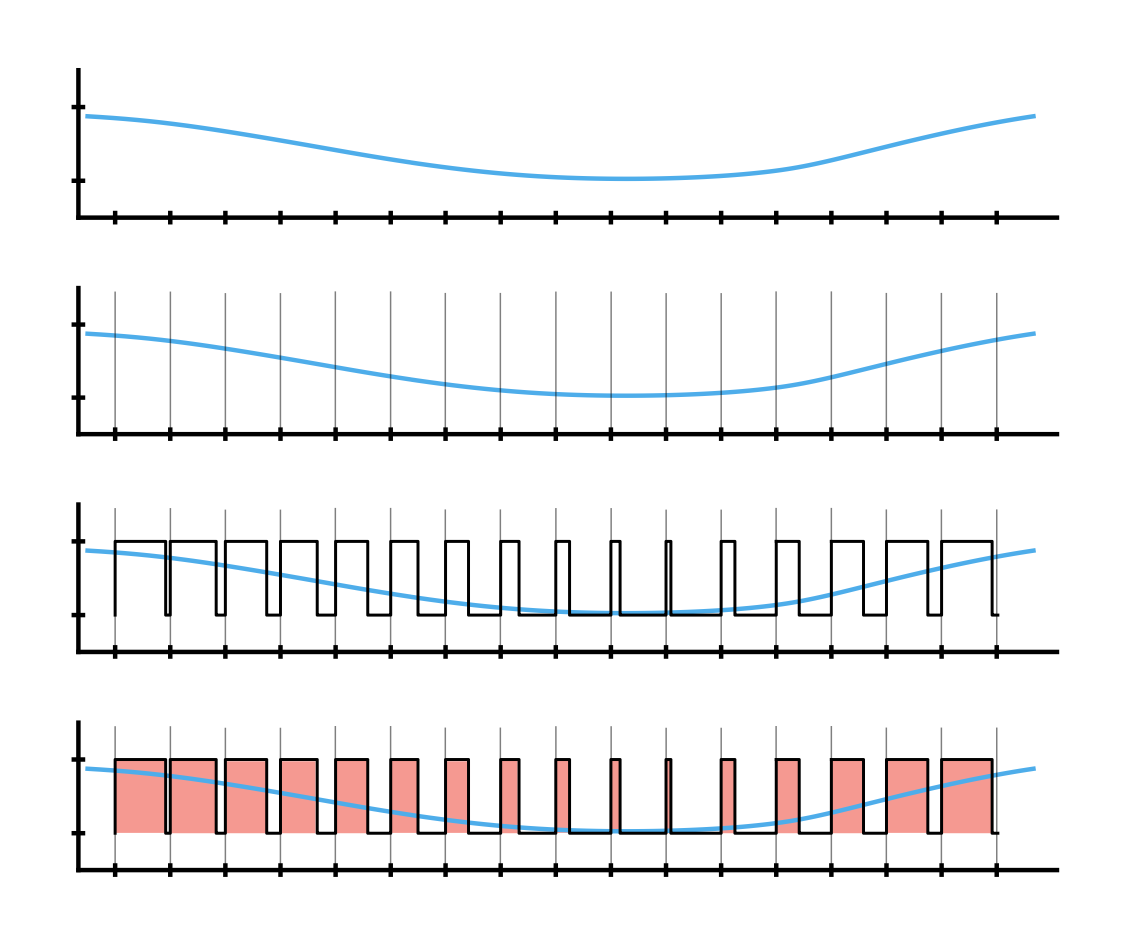
Conversions
- From an analog signal we sample at given rate and quantise with a given depth.
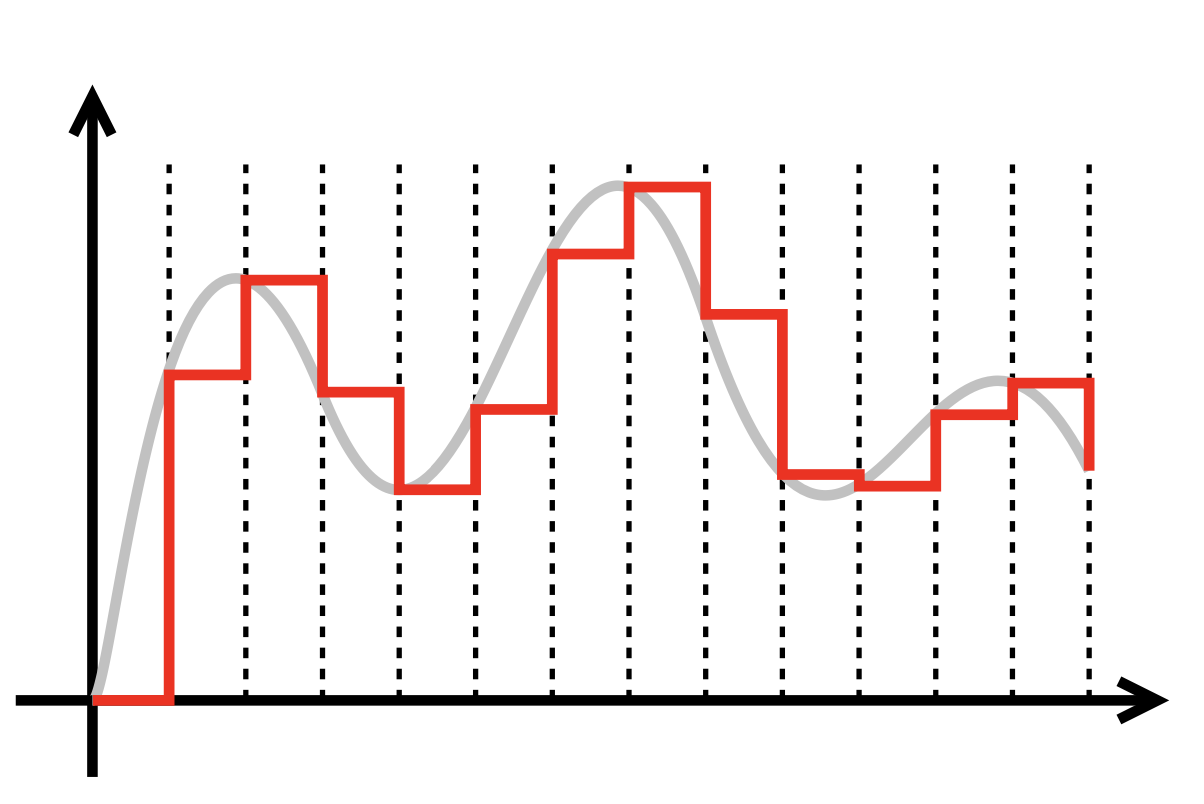
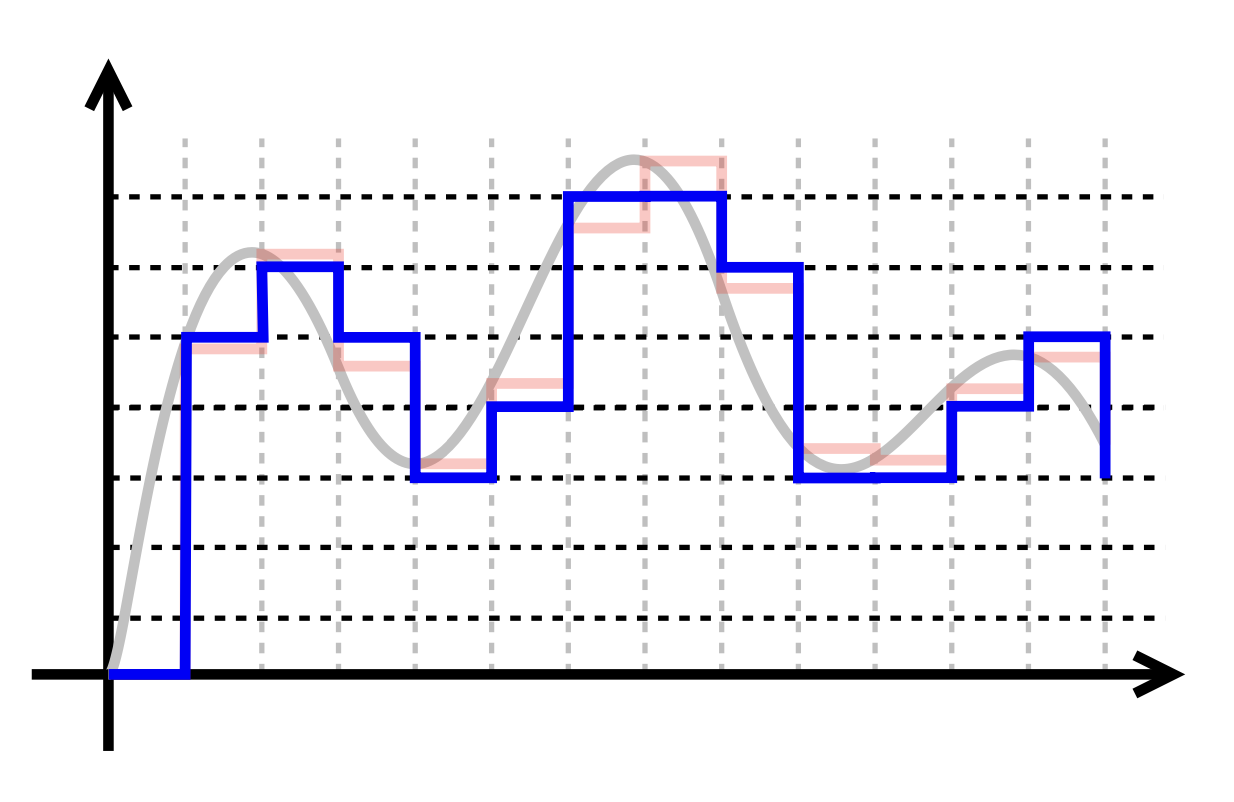
- From digital to analog we can only approximate through Pulse-Width-Modulation
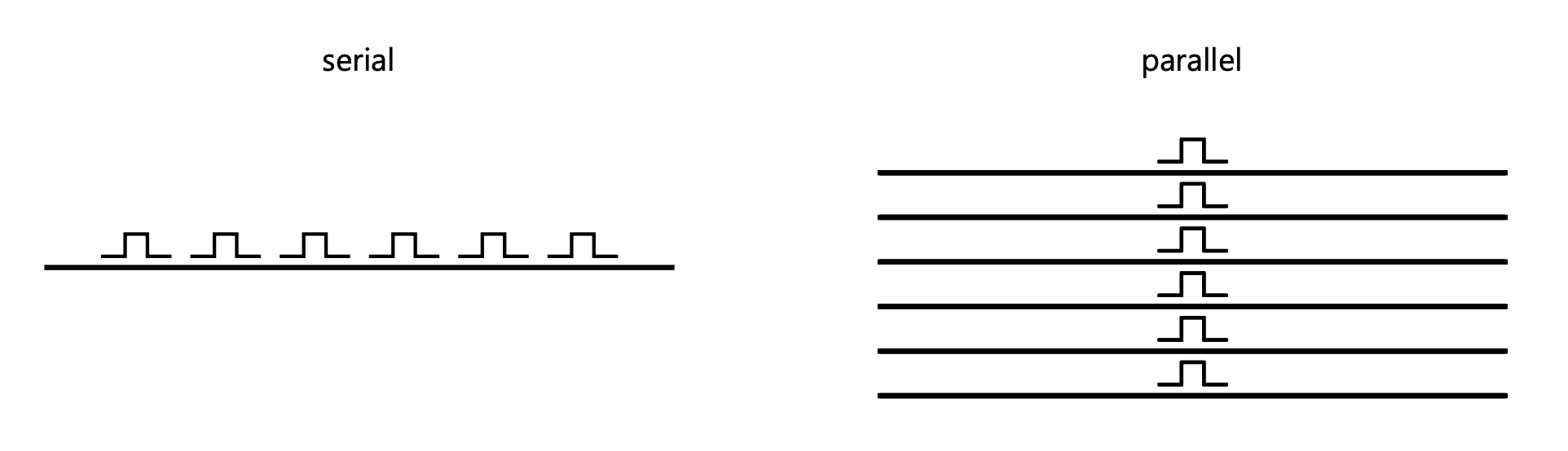
Parallel vs Serial
- When we send signals we can send them in parallel or in serial